
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/poisson-56a8fa9e3df78cf772a26eb0.jpg)
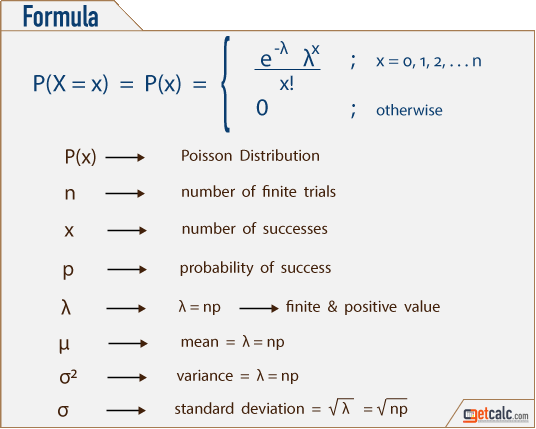
Dictionary of Statistics & Methodology: A Nontechnical Guide for the Social Sciences. Schaum’s Easy Outline of Statistics, Second Edition (Schaum’s Easy Outlines) 2nd Edition. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 31st ed. Furthermore, if you make that interval very short, with μ x > 0 and j under about 20, then the number of primes in the interval roughly follows a Poisson distribution (Croot, 2010). If you choose a random number that’s less than or equal to x, the probability of that number being prime is about 0.43 percent. Let’s say that that x (as in the prime counting function is a very big number, like x = 10 100. The Poisson Distribution formula is: P(x μ) = (e -μ) (μ x) / x! There is a connection between the Poisson distribution and the prime number theorem: Short intervals of primes fall into the approximate shape of a Poisson distribution.
#Poisson relations thermodynamics calculator software#
The usual way to calculate a Poisson distribution in real life situations is with software like IBM SPSS. The probability of 3 storms happening next year is 0.180, or 18%Īs you can probably tell, you can calculate the Poisson distribution manually but that would take an extraordinary amount of time unless you have a simple set of data.

Step 2: Plug the values from Step 1 into the Poisson distribution formula: e = 2.71828 (e is Euler’s number, a constant).x = 3 (the number of storms we think might hit next year).μ = 2 (average number of storms per year, historically).Step 1: Figure out the components you need to put into the equation. What is the probability that exactly 3 storms will hit your city next year? The average number of major storms in your city is 2 per year. Sometimes called the event rate or rate parameter. μ (the expected number of occurrences) is sometimes written as λ.The Poisson Distribution pmf is: P(x μ) = (e -μ * μ x) / x!

In addition, waste of resources is prevented. With the Poisson distribution, companies can adjust supply to demand in order to keep their business earning good profit. Hotels and restaurants could prepare for an influx of customers, they could hire extra temporary workers in advance, purchase more supplies, or make contingency plans just in case they cannot accommodate their guests coming to the area. By using this tool, businessmen are able to estimate the time when demand is unusually higher, so they can purchase more stock. Likewise, having too few stocks would still mean a lost business opportunity because you were not able to maximize your sales due to a shortage of stock. In business, overstocking will sometimes mean losses if the goods are not sold. If the average number of diners for seven days is 500, you can predict the probability of a certain day having more customers.īecause of this application, Poisson distributions are used by businessmen to make forecasts about the number of customers or sales on certain days or seasons of the year. Another example is the number of diners in a certain restaurant every day. Using this data, you can predict the probability that more books will sell (perhaps 300 or 400) on the following Saturday nights. Practical Uses of the Poisson DistributionĪ textbook store rents an average of 200 books every Saturday night. Can’t see the video? Click here to watch it on YouTube.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
